In the case of Japan, its land stretches from north to south. Climates and industries are therefore different from region to region, and appropriate renewable energy generation methods and energy demand characteristics are also different. This suggests creating different electricity grids which are distinctive from region to region so as to optimize their performance, thus leading to a basis to achieve reduced carbon emission.
For discussions to deduce better ideas, this article proposes a "Regional Grid" concept promoting electricity grids which are distinctive from region to region.
The power flow in a power system has been basically unidirectional, that is, electrical power is generated at remote and large-scale power plants then transmitted through transmission lines to demand sites and finally distributed to customers via distribution systems. Today, a large number of photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems are interconnected to various layers of the power transmission and distribution systems, and wind power generation systems and battery energy storage systems including electric vehicles (EVs) to be interconnected are increasing. They are called distributed energy resources (DERs). In this regard, the role of the power transmission and distribution systems is not only transmitting and distributing electrical energy but also exchanging it among producers and consumers.
The figure below illustrates the "Regional Grid" concept that we are proposing.
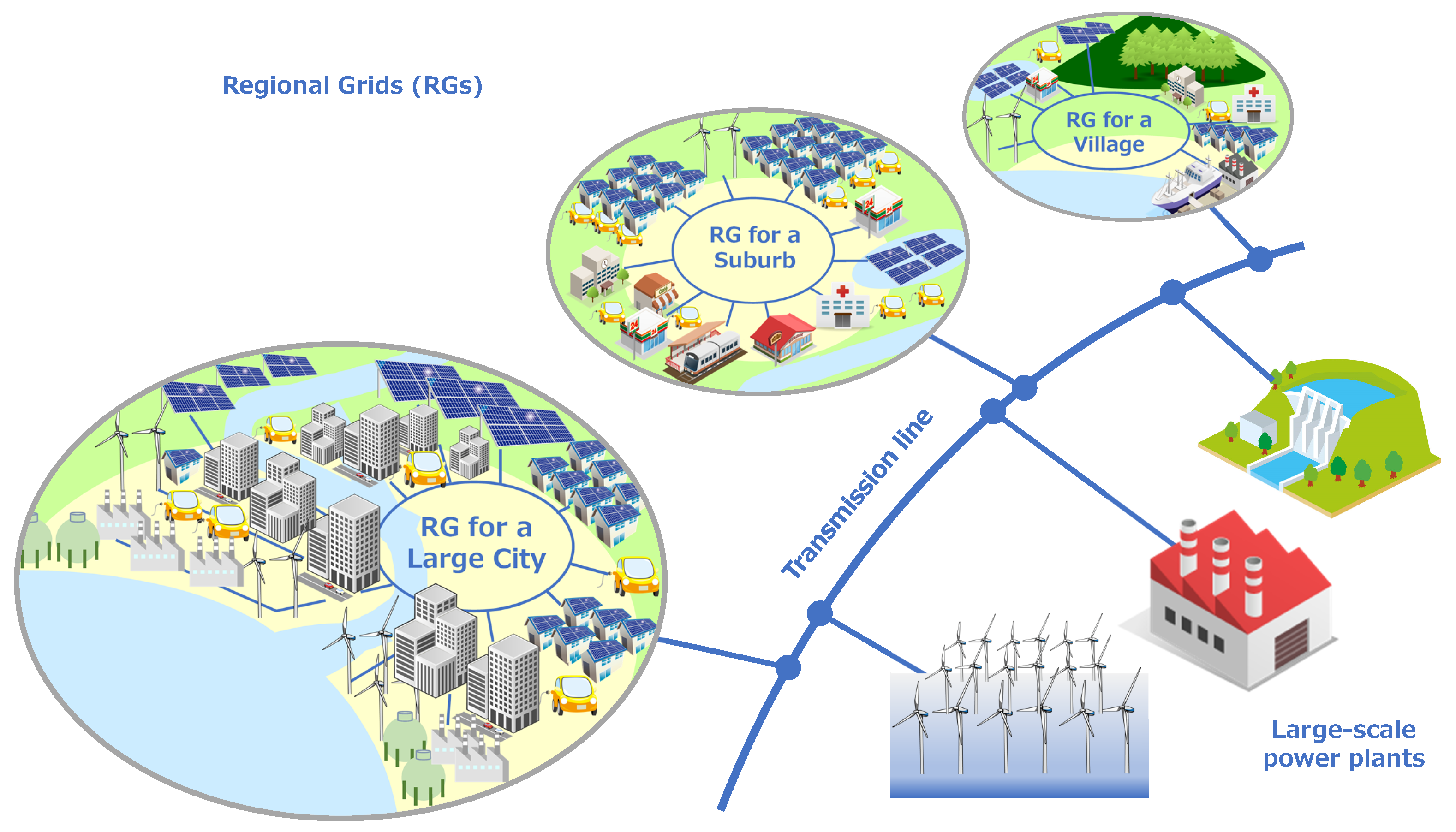
As mentioned earlier, climates, industries, appropriate renewable energy generation methods and energy demand characteristics are different from region to region. This suggests creating a distinctive electricity grid for each region so as to optimize its performance, thus leading to a basis to achieve reduced carbon emission. In the figure, three examples of regional grids are shown. Large cities are highly populated during the day time and often face the ocean with industrial areas. Suburbs with a large number of houses whose owners commute to a large city are highly populated during the night time, and those houses may be equipped with roof-top PV power generation systems. Villages which are lightly populated may have enough spaces and incentives for renewable energy production utilizing the power not only of PV and wind but also of biomass and other resources. Each region forms a regional grid for optimizing power generation and consumption. This model may fit to growing calls for the age of local autonomy today. Regional grids can never be energy-independent considering their different characteristics, and therefore they must be interconnected via transmission lines to exchange electrical energy. Large-scale power plants such as off-shore wind farms and traditional hydro and thermal generator stations are also interconnected to the transmission systems, and regional grids and large-scale power plants are coordinated to exchange electrical power at a higher level to achieve reduced carbon emission.
The Regional Grid Concept proposed above gives us a framework for investigating optimized design and operation of power grids. Prospective topics to be discussed are listed below.
At this moment, we do not have an optimization methodology which is able to consider all small electrical loads such as your computer or tablet in front of you to read this article and small PV power generation systems such as the one on top of the roof of your house in order to obtain a total optimized solution of the entire power grid. Therefore, we have to divide the large and complicated power system into layers and apply an optimization method to each layer. The Regional Grid Concept is one way to assume layers to help us create optimized design and operation methodologies. In view of this point, another way to structure power grids should be proposed and discussed, since the ultimate goal is to achieve reduced carbon emission.
© Copyright 2021 ENIC, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry. All rights reserved.