About NRRC
Organization
Activities
External Natural Event Research Team
Personnel
Approximately 60 researchers (Main Research Center: Abiko-area)
Research Fileds
External Natural Event Research Team is composed of eight specialized fields as follows.
| Assessment of Capable Fault | |
|---|---|
| Specialties of Members | Geology,Geomorphology,Seismology, Geochemistry, Geochronology, etc. |
| Main Research Topics | Evaluation of fault activity and geometry |
| Engineering Seismology | |
| Specialties of Members | Seismology, Earthquake engineering, Geomorphology, Geophysics, etc. |
| Main Research Topics | Seismic ground motion and hazard assessment |
| Geotechnical Earthquake engineering | |
| Specialties of Members | Geotechnical engineering, Geology, Seismic engineering, Reliability engineering, etc |
| Main Research Topics | Evaluation of fragility and risk for ground and slopes |
| Seismic Fragility of Structures | |
| Specialties of Members | Concrete engineering, Structural engineering, Seismic engineering, Geotechnical engineering, etc. |
| Main Research Topics | Evaluation of seismic fragility and structural soundness for civil engineering structures |
| Seismic Fragility of Building and Equipment | |
| Specialties of Members | Structural engineering, Reliability engineering, Earthquake engineering, Computational engineering, etc |
| Main Research Topics | Seismic fragility evaluations of nuclear building, equipment and piping system Seismic PRA of nuclear facilities / installations using a model plant |
| Tsunami Risk Assessment | |
| Specialties of Members | Coastal engineering, Tsunami engineering, Geology, etc. |
| Main Research Topics | Evaluation of tsunami risk and impact |
| Extreme Weather Risk Assessment | |
| Specialties of Members | Meteorology, Wind engineering, Fluid science, Structural engineering, etc. |
| Main Research Topics | Evaluation for tornado and other extreme meteorological risk and development of protective measures |
| Volcanic Risk Assessment | |
| Specialties of Members | Geology, Volcanology, Fluid science, Meteorology , etc. |
| Main Research Topics | Evaluation of volcanic ash-fall risk |
Main Research Facilities
Large-scale Tsunami Physical Simulator
The large-scale tsunami physical simulator is a facility designed with the main purpose of assessing the impact resulting from a tsunami on a nuclear power generation facility, and is the only facility in the world capable of precisely reproducing on a large scale the water flow of a tsunami running up onto land.
With this simulator, a wide variety and large number of tests have been conducted, including verifying the performance of installed barriers equivalent to actual seawall embankments inside a channel as well as measuring the force of debris impact ro structures by using full-scale vehicles.
 |
 |
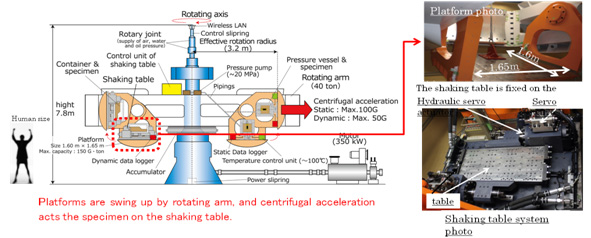
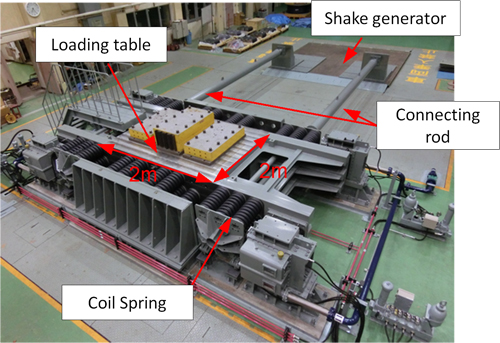
Strong Shake Generator: Resonance-type shaking table
In order to assess the seismic safety of components, pipes and equipments in nuclear power plants, CRIEPI has developed a novel shaking table with the capability to conduct vibration testing up to the peak acceleration of 20G. Such a highly-accelerated condition can be realized in this device by using resonance phenomena (which one can observe, for example, in building motion subject to earthquake or wind forces synchronizing with the inherent motion period of the building).
Since the standard earthquake ground motion to be employed in seismic design has been updated more stringently, the response acceleration of the equipment tends to exceed the response acceleration that has been previously obtained in shaking tests for confirmation of safe operation at the locations where the equipment is mounted. Furthermore, from the standpoint of equipment fragility in earthquake PRA, fragility assessments need to be conducted to the extent such that extreme acceleration brings about actual damage in shaking tests. Based on these backgrounds, this strong shake generator is used to perform tests to verify such as the functionality of electric-actuated valves attached to pipes, etc.
 |
Helical X-ray CT Scanner
This scanner allows for a nondestructive three-dimensional analysis of the internal structure of rock formations, deposits and other samples. Currently, in assessments of tsunami as well as fault activity that focus on nuclear power facilities, three-dimensional structural analysis of fault fracture zones and tsunami deposits are being conducted. In addition, in order to clarify the origin and process of formation of geological structures in the ground which forms the foundation of nuclear power facilities, tests have been conducted with scale models of actual fault displacement. This scanner has provided a three-dimensional image of ground displacement of the scale ground.
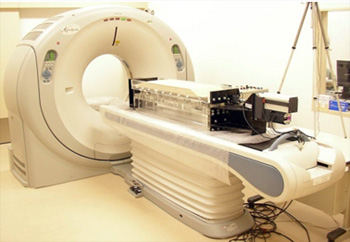
(Scanner with a strike-slip fault model experimental apparatus set)
Centrifugal Vibration Table
In order to contribute to the development of seismic stability assessments of the foundation ground of a nuclear power facility and its surrounding slopes, a vibration table (unidirectional vibration) has been installed on the platform for the CRIEPI’s centrifugal base rock simulator platform. This enables simulation of the stress during an actual earthquake to be reproduced by imparting centrifugal force on a scale model of the foundation ground and surrounding slopes. This table is capable of reproducing an earthquake of 500gal - 1000gal with a 1/25th - 1/50th scale model of the ground. The size of the vibration table on which the model is placed is 30cm x 70cm, and the maximum payload is 500kg.